LSAT 123 – Section 3 – Question 22
LSAT 123 - Section 3 - Question 22
June 2007You need a full course to see this video. Enroll now and get started in less than a minute.
Target time: 1:34
This is question data from the 7Sage LSAT Scorer. You can score your LSATs, track your results, and analyze your performance with pretty charts and vital statistics - all with a Free Account ← sign up in less than 10 seconds
| Question QuickView |
Type | Tags | Answer Choices |
Curve | Question Difficulty |
Psg/Game/S Difficulty |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT123 S3 Q22 |
+LR
| Must be true +MBT Conditional Reasoning +CondR | A
6%
149
B
40%
150
C
46%
154
D
5%
147
E
3%
146
|
140 156 171 |
+Harder | 144.044 +SubsectionEasier |
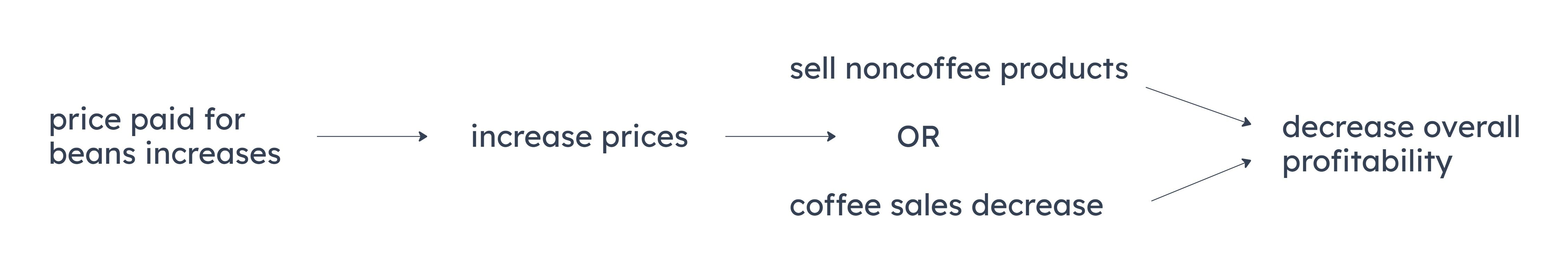
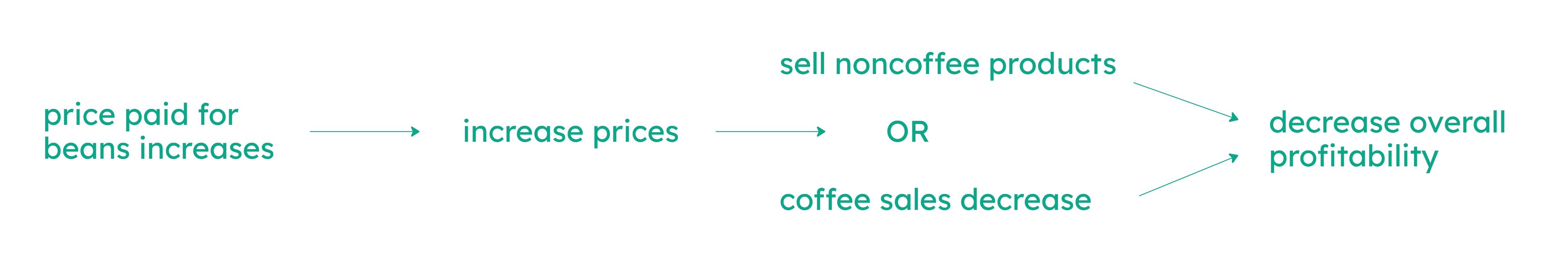
If the Coffee Shoppe increases its prices, then there will be a decrease in overall profitability.
If the price paid for beans increases, the Coffee Shoppe will either sell non-coffee products or coffee sales will decrease.
A
If the Coffee Shoppe’s overall profitability decreases, the price it pays for coffee beans will have continued to increase.
B
If the Coffee Shoppe’s overall profitability decreases, either it will have begun selling noncoffee products or its coffee sales will have decreased.
C
The Coffee Shoppe’s overall profitability will decrease if the price it pays for coffee beans continues to increase.
D
The price it pays for coffee beans cannot decrease without the Coffee Shoppe’s overall profitability also decreasing.
E
Either the price it pays for coffee beans will continue to increase or the Coffee Shoppe’s coffee sales will increase.
Relevant lessons: Referential phrasing | Modifiers and embedded clauses | Conditional logic | Advanced logic | Must be true questions
Take PrepTest
Review Results
LSAT PrepTest 123 Explanations
Section 1 - Reading Comprehension
- Passage 1 – Passage
- Passage 1 – Questions
- Passage 2 – Passage
- Passage 2 – Questions
- Passage 3 – Passage
- Passage 3 – Questions
- Passage 4 – Passage
- Passage 4 – Questions
Section 2 - Logical Reasoning
- Question 01
- Question 02
- Question 03
- Question 04
- Question 05
- Question 06
- Question 07
- Question 08
- Question 09
- Question 10
- Question 11
- Question 12
- Question 13
- Question 14
- Question 15
- Question 16
- Question 17
- Question 18
- Question 19
- Question 20
- Question 21
- Question 22
- Question 23
- Question 24
- Question 25
Section 3 - Logical Reasoning
- Question 01
- Question 02
- Question 03
- Question 04
- Question 05
- Question 06
- Question 07
- Question 08
- Question 09
- Question 10
- Question 11
- Question 12
- Question 13
- Question 14
- Question 15
- Question 16
- Question 17
- Question 18
- Question 19
- Question 20
- Question 21
- Question 22
- Question 23
- Question 24
- Question 25
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment. You can get a free account here.