Technician: Laboratory mice that are used for research aimed at improving human health are usually kept in small cages. Such an environment is neither normal nor healthy for mice. Moreover, the reliability of research using animals is diminished if those animals are not in an environment that is normal for them.
Summary
Keeping animals in an environment that isn’t normal for them reduces the reliability of the research that those animals are used in.
Lab mice that are used in research for human health are usually kept in small cages.
Small cages are not a normal or healthy environment for mice.
Very Strongly Supported Conclusions
Keeping lab mice in small cages reduces the reliability of the research that those mice are used in.
The reliability of research for human health using lab mice is diminished because the mice are kept in small cages.
A
The conditions under which laboratory mice are kept are not likely to change in the near future.
Unsupported. We only know that lab mice used in research for human health are usually kept in small cages currently. This might or might not change in the near future.
B
If laboratory mice were kept under better conditions, it would be appropriate to use them for research aimed at improving human health.
Unsupported. The reliability of current health research is reduced because mice are kept in small cages. But we don't know how better conditions would impact the research. The technician also doesn’t mention whether it's "appropriate" to use lab mice for research.
C
Research using laboratory mice that is aimed at improving human health is compromised by the conditions under which the mice are kept.
Very strongly supported. Human health research using lab mice is compromised because the mice are kept in an environment that isn’t normal for them, which reduces the reliability of the research they’re used in.
D
Those who conduct research aimed at improving human health will develop new research techniques.
Unsupported. The technique of using lab mice is unreliable because the mice are kept in small cages. But the technician doesn’t say anything about whether researchers will develop new techniques.
E
Laboratory mice that are used for research that is not directly related to human health are not usually kept in small cages.
Unsupported. We only know that lab mice that are used in research that is directly related to human health are usually kept in small cages. We don’t know anything about the conditions of lab mice used in other research.
A
“production cost” in the definition of dumping refers to the cost of producing the product in the country where it originates or in the country where it is sold
B
there is agreement among experts about whether dumping is harmful to the economy of the country in which products are sold for less than production cost
C
shrimp producers from Country F charge more for shrimp that they sell within their own country than for shrimp that they sell in Country G
D
shrimp producers from Country F will eventually go out of business if they continue to sell shrimp in Country G for less than production cost
E
shrimp producers from Country F are selling shrimp in Country G for considerably less than production cost or just slightly less
A
People’s opinions never change very much.
B
A minority of Denmark’s population feels that banning cigarette advertising would set a bad precedent.
C
Most of Denmark’s population is not seriously concerned about cigarette advertising.
D
Most of Denmark’s population favors some sort of ban on cigarette advertising.
E
Most of Denmark’s population does not smoke cigarettes.
Mary: There are already too few part-time jobs for students who want to work, and simply requiring students to work will not create jobs for them.
A
It analyzes an undesirable result of undertaking the course of action that Tom recommends.
B
It argues that Tom has mistaken an unavoidable trend for an avoidable one.
C
It provides information that is inconsistent with an explicitly stated premise in Tom’s argument.
D
It presents a consideration that undercuts an assumption on which Tom’s argument depends.
E
It defends an alternative solution to the problem that Tom describes.
The stimulus can be diagrammed as follows:
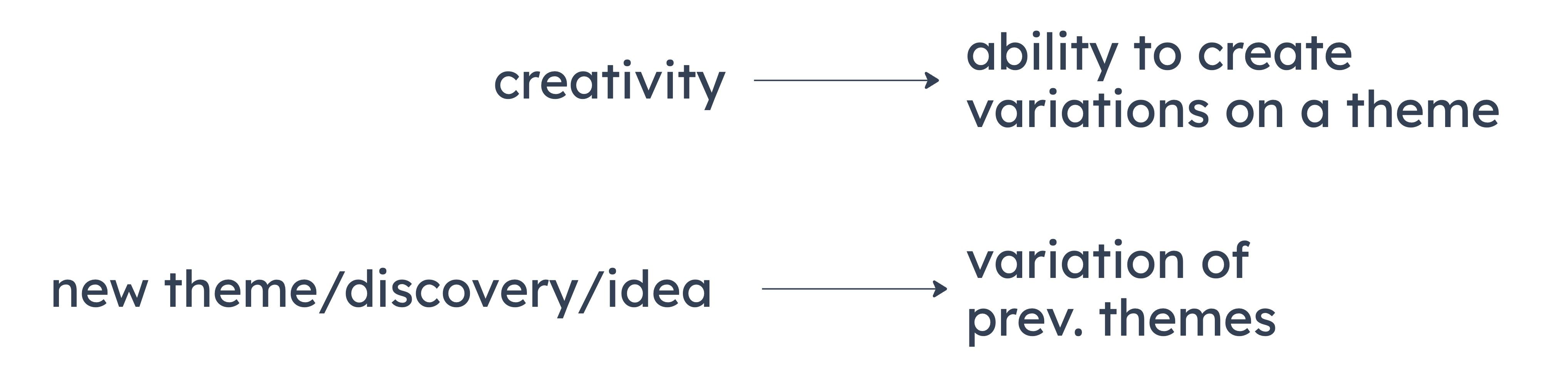
Some examples of valid logical inferences from the stimulus are: there are no new themes which are not built on existing themes, and if one lacks the ability to modify a theme, they lack creativity.